

A urine drug test may only test positive for cocaine for about 4 days after last use. You doctor may use a drug test to confirm cocaine use. Sometimes a health event, such as a seizure or stroke, will prompt a doctor to bring up the possibility of cocaine addiction to you if you also have other symptoms. It’s important to be straightforward and honest so you can get the right treatment. If you reach out to your doctor about your cocaine use, they will start by asking you questions about your lifestyle, habits, usage, and dosage.
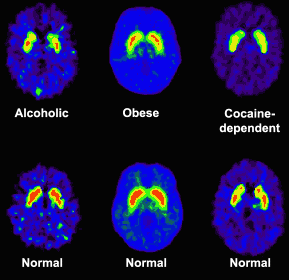
How do doctors diagnose cocaine addiction? Disulfiram (Antabuse) is one such medication. There’s currently no medication that treats cocaine addiction, but sometimes doctors prescribe drugs off-label to treat it. There are different treatment options available for people who need help stopping cocaine use.Ĭognitive behavioral therapy, outpatient and inpatient treatment, drug-free communities, and 12-step programs (such as Cocaine Anonymous and Narcotics Anonymous) are all options. This seemed to imply that 5 months without cocaine would restore much of what was lost in terms of brain function. The amount of normal cognition you regain will vary depending on several factors, like:Ī small 2014 study found that as long as cocaine use was moderate and recovery began within 1 year, brain damage from cocaine use was at least partially reversible.Īnd a 2014 review suggests many of the long-term cognitive effects of cocaine use are actually connected to withdrawal from cocaine. Your brain may be able to recover from the effects of cocaine use. People who regularly use cocaine lose more than twice that in a year, according to a 2012 study.Ĭocaine use in young adults also changes the shape of neurons and synapses as the developing brain tries to protect itself, according to research from 2009.ĭoes the brain recover from the effects of cocaine use? The typical brain loses 1.69 milliliters of gray matter each year as part of the aging process. The impact of cocaine on your brain cells becomes even more significant as you age. It can also starve your brain of the blood it needs, which kills brain cells. It can cause your heart rate to fall out of rhythm. This stresses your cardiovascular system. Since cocaine causes your blood vessels to narrow, your heart has to work harder to pump blood to your brain. When the brain’s “cleanup processes” are sped up or disrupted from cocaine, brain cells are essentially thrown out.Ĭocaine damages your brain in other ways, too. That can cause the neurons in your brain to work more slowly or begin to die off.Ī 2016 study in the brains of mice gave more insight into this phenomenon. That’s why heavy cocaine use can lead to seizure disorders and other neurological conditions.Ĭocaine use slows the glucose metabolism in your brain as well. Over time, flooding your brain with dopamine can damage the structure of the brain. That means larger amounts of cocaine are necessary to produce the same effects of a dopamine high. Over time, cocaine causes your brain to becomes less sensitive to dopamine. This excess dopamine blocks your brain cells from communicating with one another. When you’re using cocaine, dopamine floods your brain cells, but then it doesn’t have anywhere else to go. Small doses of dopamine travel through your brain cells to indicate pleasure or satisfaction. Why does cocaine specifically affect your brain?Ĭocaine increases the amount of a chemical called dopamine in your brain. Sometimes, the long-term side effects of cocaine use are a sign of brain damage. But long term side-effects can be permanent. Most short-term side effects of cocaine wear off within a day or two. movement disorders, including Parkinson’s disease.Long-term ways cocaine can affect the brain include: a temporary feeling of intense happiness or pleasureĬocaine can have long-term side effects, too, especially after prolonged, habitual use.Other common, short-term effects of cocaine include: That in turn boosts your alertness, leaving you feeling a “high” from the drug. Like other stimulants, cocaine gives you an energy surge. That means it affects the central nervous system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
